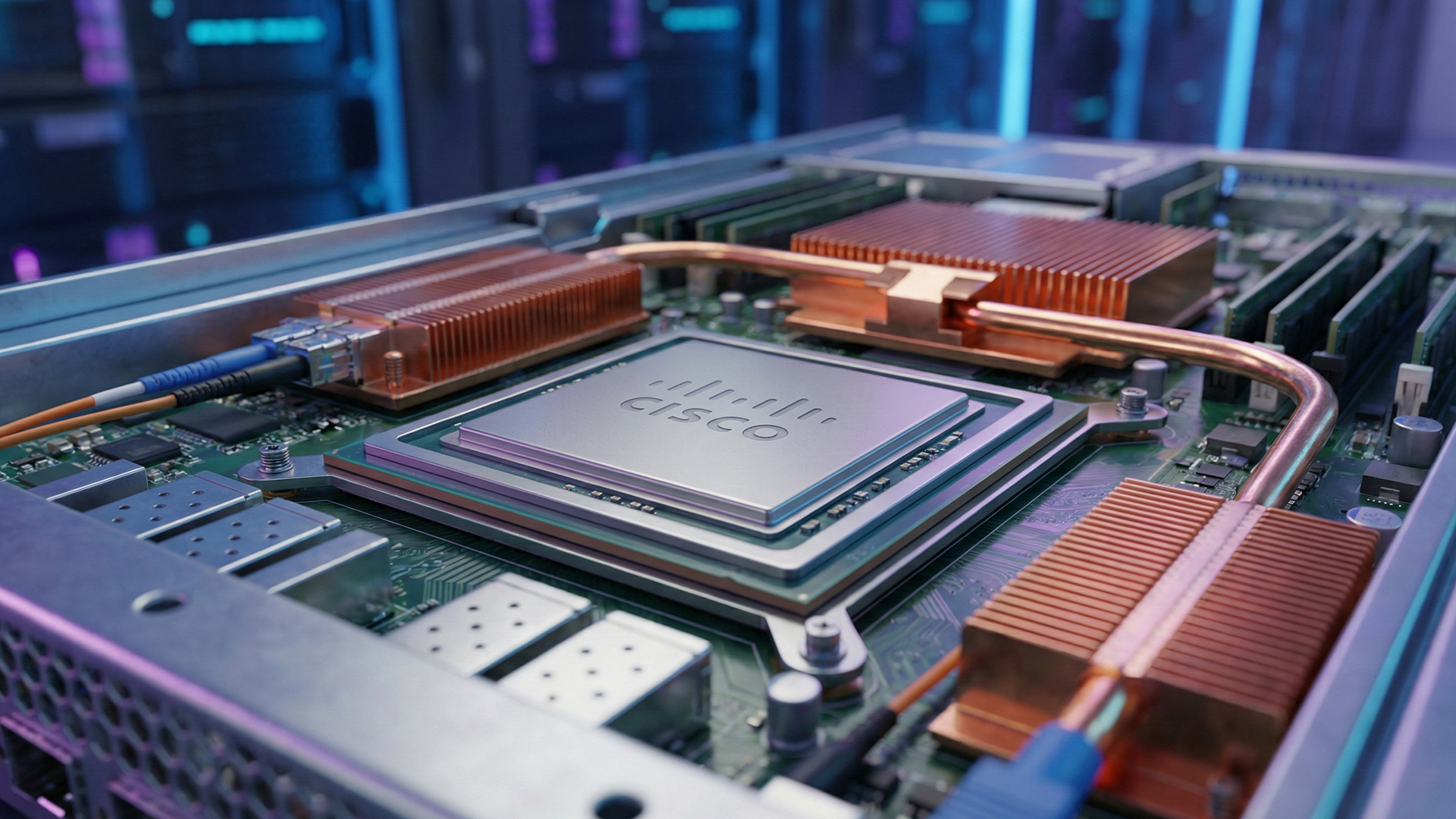
Cisco Systems has launched a powerful new networking chip and router system designed specifically for artificial intelligence workloads, marking a major push into the AI infrastructure market. The move puts Cisco in direct competition with industry leaders Nvidia and Broadcom.
The chip, called Silicon One G300, is built to handle massive amounts of data traffic within AI data centres, where thousands of processors must work together at extremely high speeds. Efficient data flow is critical in these environments to ensure AI models train and run smoothly.
Cisco says the G300 will be made using 3‑nanometer technology by TSMC and is expected to hit the market in the second half of 2026. One of its standout features is its ability to automatically reroute data during sudden traffic spikes, which Cisco calls a “shock absorber” function. This innovation can boost performance for certain AI tasks by nearly 30%, according to the company.
This launch highlights how networking technology is becoming just as important as GPUs or AI processors themselves. In large AI clusters, even a small slowdown in data movement can affect overall performance. By focusing on high-speed, intelligent networking, Cisco hopes to give enterprises and cloud providers a way to optimize their AI systems.
The G300 directly competes with Broadcom’s Tomahawk line and Nvidia’s AI networking solutions, aiming to win over both hyperscale cloud providers and enterprises building their own AI clusters.
As AI continues to drive growth in computing infrastructure, faster and more efficient networking solutions are becoming essential. Cisco’s new chip signals its ambition to be a key player in the $600 billion AI infrastructure market, showing that smart network design is now a critical part of the AI revolution.
Also Read: 10 killed in Canada school shooting